CONTROL FUNDAMENTALS
Knowledge of input and output options is necessary for understanding control functions.
Input Options
Signal may be either closed contacts or applied voltage.
- Power Control
Besides powering the unit’s internal circuitry, input power may be used as the control signal. - Isolated Control
An independent input used as control signal. - Pulse Control
Unit’s internal circuit latches isolated control signal. An alternate control may be required to reset the unit. - Totalized Control
The elapsed delay time and output state are retained in memory while control and/or power is off; allowing the sum total of control ON time to be used to control output. - Reset Control
Some units are equipped with an isolated control input to reset the delay time and output. - Stop Control
Suspension of delay time may be accomplished with an isolated control on some units.
Output Options
Output may be relay contacts or solid state voltage.
- Timed Output
Output is controlled by unit function and delay time setting. - Instant Output
Output directly follows the input control signal.
Reset Options
Elapsed delay time is typically reset when the control signal turns on.
- Totalized Control
The elapsed delay time and output state are retained in memory while control and/or power is off; allowing the sum total of control ON time to be used to control output. - Power Outage
Battery backed up memory retains elapsed time and output state through power failures. - Stop Control
Suspension of delay time may be accomplished with an isolated control on some units.
ON DELAY
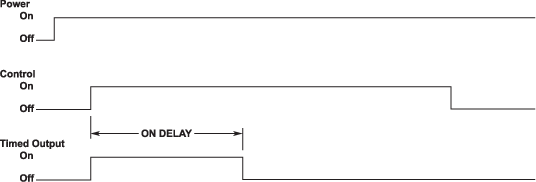
Delays energizing the output. Also known as time delay, delay on make, delay on operate, delay on energization or slow operate.
- Control is independent of unit power.
When control turns on, delay time elapses before output turns on. The output remains on until the unit is reset either by turning off power or control.
- The output remains on until the unit is reset either by turning off power or control.
OFF DELAY
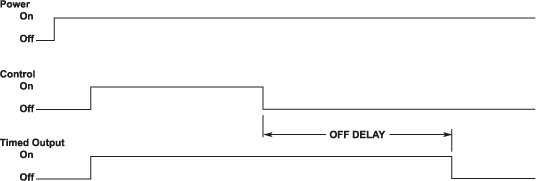
Delays de-energizing the output. Also known as delay on break, delay on release, delay on de-energization or slow release.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, the output turns on.
- When the control turns off, the delay starts and output turns off after time elapses.
- Delay time resets when control turns on.
INTERVAL
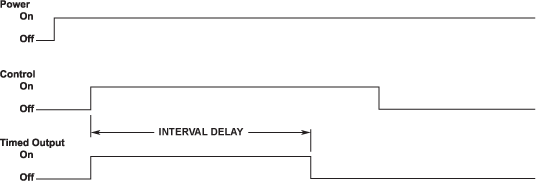
Control initiated, timed interval output. Also known as one shot, maintained interval or interval on.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, output turns on and delay time elapses before output returns to normal.
- If control changes during the delay time period, the output turns off and the delay time resets.
ONE CYCLE
Control initiated, delayed interval output.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, delay time elapses before output turns on.
- The delay then restarts and output turns back off once time has elapsed.
REPEAT CYCLE—ON START
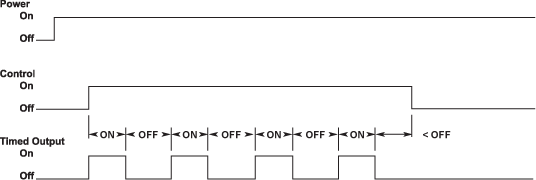
Control initiated, Dual time repeating on-off cycle.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, the output turns on while ON time elapses. The output then turns back off while OFF time elapses.
- This cycle then repeats until power is removed from the unit or control turns off.
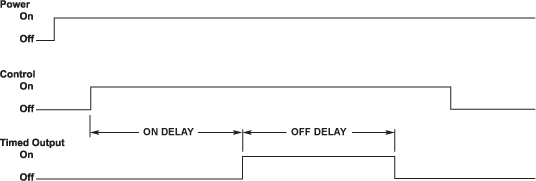
ON DELAY/OFF DELAY
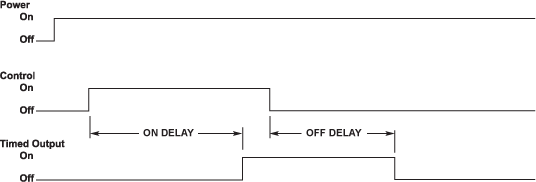
Control initiated, Dual time combination of On Delay and Off Delay timers.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, delay time elapses before output turns on.
- When the control turns off, the delay starts and output turns off after time elapses.
- Delay time resets when control turns on.
MOTION DETECTION
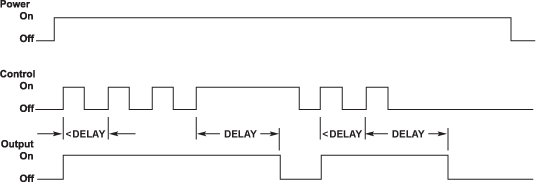
Minimum frequency of pulses indicates normal or safe operation.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- When control turns on, output turns on and delay time starts.
- The time delay restarts each time the control is turned on.
- As long as two control pulses occur within the delay time the output remains on.
- If the control pulses occur to slowly, the delay will time out and the output turns off.
- Turning off unit power resets the unit.
PLC WATCHDOG
Motion detectors which accept a voltage as control pulse are able act as a PLC process watchdog.
COUNTER
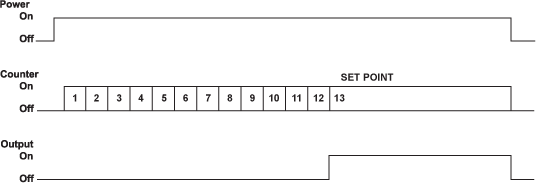
Count set point dictates output.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- Input pulses are counted and displayed digitally.
- Output comes on and set point count remains displayed once count is reached.
- Turning off unit power resets the unit.
RESISTANCE/VOLTAGE DETECTION
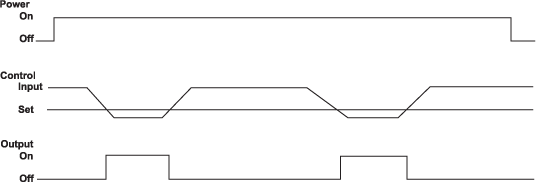
Resistance below a set point turns on the output.
- Control is independent of unit power.
- Output is on as long as the input remains greater than the set point.
- Once the input drops below the set point the output is turned off.
